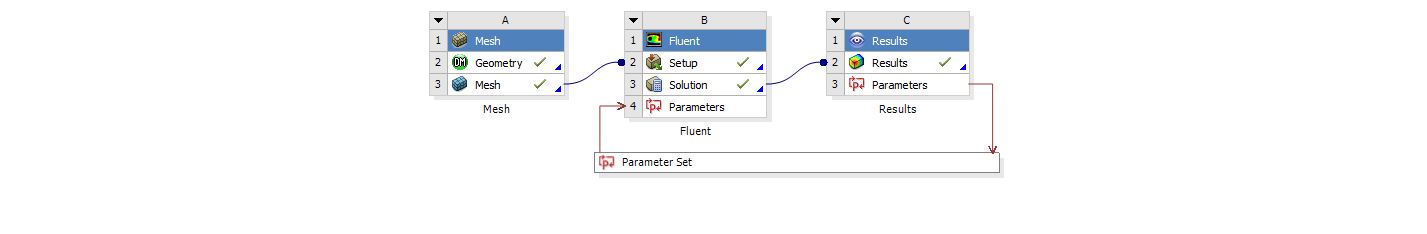
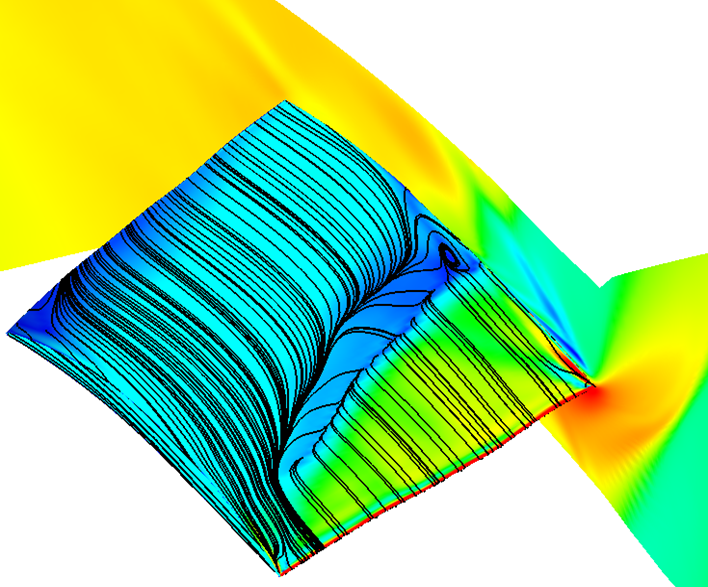
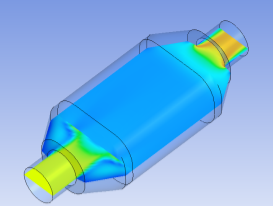
Our support team is tasked with helping our customers to extract maximum value from their CFD simulations, and we are always striving to help customers who work at the bleeding edge of CFD. A common question is: How can I drive Fluent UDF parameters directly from ANSYS Workbench? The ANSYS Fluent User Defined Function (UDF)...
How can I drive Fluent UDF Parameters directly from ANSYS Workbench?